Create a read-only user in Kubernetes
Normal users are assumed to be managed by an outside, independent service. Kubernetes does not have objects which represent normal user accounts. Normal users cannot be added to a cluster through an API call. However, any user that presents a valid certificate signed by the cluster's certificate authority (CA) is considered authenticated. So we can create a user with read-only access to the cluster, and hand the kube config file over to that that user.
This post assumes a basic level of understanding of how Kubernetes works.
Create a ClusterRole
First create a ClusterRole. I've decided to name the cluster role 'kube-reader-cluster-role' As you can see I excluded 'secrets'.
You can find out about apiGroups, resources and verbs with the following command:
More info about ClusterRoles and RBAC you can find here. This is the result:
1cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
2apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
3kind: ClusterRole
4metadata:
5 name: kube-reader-cluster-role
6rules:
7- apiGroups: [""]
8 resources: ["pods","configmaps","services","events","namespaces","nodes","limitranges","persistentvolumes","persistenttvolumeclaims","resourcequotas"]
9 verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
10- apiGroups:
11 - apps
12 resources: ["*"]
13 verbs:
14 - get
15 - list
16 - watch
17EOF
Create a certificate request
Let's add read-only access for a user called kube-support. It's not a real name. This user kube-support should be able to access Kubernetes resources from outside the cluster and they are only allowed to read.
1openssl req -new -newkey rsa:4096 -nodes -keyout kube-support.key -out kube-support.csr -subj "/CN=kube-support/O=readers"
2csr=$(cat kube-support.csr | base64 | tr -d '\n')
Present the certificate signing request to Kubernetes like so:
1cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
2apiVersion: certificates.k8s.io/v1
3kind: CertificateSigningRequest
4metadata:
5 name: kube-support-reader-access
6spec:
7 signerName: kubernetes.io/kube-apiserver-client
8groups:
9 - system:authenticated
10 request: $csr
11 usages:
12 - client auth
13EOF
Then check the progress:
1k get certificatesigningrequests.certificates.k8s.io
2
3NAME AGE SIGNERNAME REQUESTOR CONDITION
4kube-support-reader-access 19s kubernetes.io/kube-apiserver-client system:admin Pending
Of course the state will be Pending unless you approve it. So let's go ahead and approve the csr:
1kubectl certificate approve kube-support-reader-access
2# certificatesigningrequest.certificates.k8s.io/kube-support-reader-access approved
Retrieve the crt
1kubectl get csr kube-support-reader-access -o jsonpath='{.status.certificate}' | base64 --decode > kube-support.crt
Build the kube config file.
Not sure if you ever studied the ~/.kube/config file up close. It has the following structure:
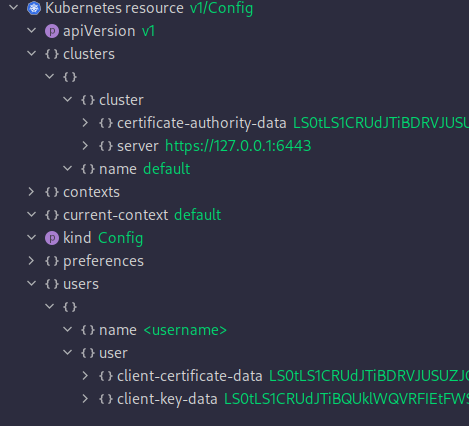
config
So our next job is to populate the necessary fields. Let's start with certificate-authority-data:
1kubectl config view -o jsonpath='{.clusters[0].cluster.certificate-authority-data}' --raw | base64 --decode - > k8s-ca.crt
Create the initial kube config file and populate it with the certificate-authority-data
1kubectl config set-cluster $(kubectl config view -o jsonpath='{.clusters[0].name}') --server=$(kubectl config view -o jsonpath='{.clusters[0].cluster.server}') --certificate-authority=k8s-ca.crt --kubeconfig=kube-support-config --embed-certs
Let's add the client-certificate-data and client-key-data.
1kubectl config set-credentials kube-support --client-certificate=kube-support.crt --client-key=kube-support.key --embed-certs --kubeconfig=kube-support-config
Set a context (just default)
1k config set-context default --cluster=$(kubectl config view -o jsonpath='{.clusters[0].name}') --namespace=default --user=kube-support --kubeconfig=kube-support-config
Switch to the namespace
We are now done with the kube config file.
Check if it works
1k get pods --kubeconfig kube-support-config
2Error from server (Forbidden): pods is forbidden: User "kube-support" cannot list resource "pods" in API group "" in the namespace "default"
It doesn't work. We should bind the kube-support user to the kube-reader-cluster-role.
1k create clusterrolebinding kube-support-kube-reader --clusterrole=kube-reader-cluster-role --user=kube-support
2# clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kube-support-kube-reader created
Now let's try again:
1k run -it trouble-pod --image=debian --kubeconfig kube-support-config
2Error from server (Forbidden): pods is forbidden: User "kube-support" cannot create resource "pods" in API group "" in the namespace "default"
Well this was expected. kube-support has only read permissions! Let's try something else!
Success!
1k get pods --kubeconfig kube-support-config --all-namespaces
2NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
3ingress-nginx ingress-nginx-admission-create-cxb7c 0/1 Completed 0 46h
4ingress-nginx ingress-nginx-admission-patch-zssrb 0/1 Completed 1 46h
5kube-system metrics-server-7b4f8b595-42s5m 1/1 Running 4 46h
6kube-system coredns-66c464876b-zckdd 1/1 Running 3 46h
7ingress-nginx ingress-nginx-controller-57fb49bdbf-xcpmd 1/1 Running 20 46h
8kube-system local-path-provisioner-7ff9579c6-shd4b 1/1 Running 28 46h
9bob trouble-pod 1/1 Running 1 39m
10
Resources
https://codefarm.me/2019/02/01/access-kubernetes-api-with-client-certificates/ https://ahmet.im/blog/mastering-kubeconfig/ https://medium.com/swlh/how-we-effectively-managed-access-to-our-kubernetes-cluster-38821cf24d57 https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/certificate-signing-requests/#authorization https://www.cyberark.com/resources/threat-research-blog/securing-kubernetes-clusters-by-eliminating-risky-permissions https://www.openlogic.com/blog/granting-user-access-your-kubernetes-cluster